Proxies and VPNs both offer ways to browse the web anonymously. But they serve different purposes and have distinct features.
Understanding these differences can help you choose the right tool for your needs. Proxies act as intermediaries between your device and the internet. They hide your IP address by routing your traffic through another server. VPNs, or Virtual Private Networks, do more than just hide your IP.
They encrypt your entire internet connection, providing an extra layer of security. This means VPNs offer better privacy and protection compared to proxies. Knowing these key differences can help you make an informed decision for online privacy and security.

Credit: www.fortinet.com
How Proxies Work
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet. It receives your request to access a website, then forwards it to the site on your behalf. The website responds to the proxy server, which then sends the data back to you. This process hides your real IP address, providing a layer of anonymity.
Proxies can filter content and improve security. They can also cache data to speed up access to frequently visited sites. Different types of proxies offer varied levels of privacy and performance. Let’s explore these types and their use cases.
Types Of Proxies
There are several types of proxies. Each serves a unique purpose.
1. HTTP Proxies: These handle web traffic. They are ideal for accessing geo-blocked content.
2. HTTPS Proxies: These are secure and encrypt your data. They are suitable for sensitive transactions.
3. SOCKS Proxies: These work with any traffic type. They are often used for activities like gaming and video streaming.
4. Transparent Proxies: These do not hide your IP address. They are usually used in schools and offices for monitoring.
Use Cases For Proxies
Proxies have various practical applications.
1. Accessing Restricted Content: Proxies allow you to bypass geo-restrictions. This is useful for streaming services or news sites.
2. Enhancing Privacy: Proxies can hide your IP address. This makes it harder for websites to track your online activity.
3. Improving Security: Proxies can filter malicious content. This helps protect your device from harmful websites.
4. Load Balancing: Proxies can distribute web traffic. This helps manage high volumes of requests and prevents server overload.
5. Caching: Proxies store copies of frequently accessed websites. This speeds up load times for users.
How Vpns Work
Understanding how VPNs work can be a game-changer for anyone looking to secure their online activities. VPNs, or Virtual Private Networks, act like a secure tunnel that connects your device to the internet, encrypting your data along the way. Imagine having a secret passageway that only you can use; that’s what a VPN does for your online presence. Now, let’s dive deeper into the nitty-gritty of VPNs and explore their different types and uses.
Types Of Vpns
VPNs come in different flavors, each catering to specific needs. Here are the main types:
- Remote Access VPN: This type allows users to connect to a private network from a remote location. It’s perfect for employees who need to access company resources from home or while traveling.
- Site-to-Site VPN: Often used by businesses with multiple offices, this VPN connects entire networks to each other. Think of it as a bridge linking different islands of data.
- Client-to-Server VPN: This is a direct connection between a user’s device and a specific server. It’s like having a dedicated lane on the internet highway.
Use Cases For Vpns
So, when and why would you use a VPN? Let’s break it down:
- Security on Public Wi-Fi: Ever used free Wi-Fi at a coffee shop? A VPN can protect your data from prying eyes.
- Accessing Restricted Content: Want to watch a show not available in your country? A VPN can make it seem like you’re browsing from another location.
- Bypassing Censorship: In some countries, certain websites are blocked. A VPN can help you access them by masking your real location.
- Secure Remote Work: If you work from home, a VPN can ensure that your company’s sensitive information stays safe.
So, whether you’re trying to sneak past geo-blocks or just want to keep your data secure, VPNs have got you covered. They offer a versatile and robust solution for a variety of online challenges.
And hey, if you ever find yourself in a pickle, remember that a VPN is like your trusty sidekick, always ready to save the day!
Security Features
When it comes to online security, understanding the difference between a Proxy and a VPN is crucial. Both serve to protect your online identity, but they do so in different ways. This section dives deep into the key security features of both proxies and VPNs, shedding light on their encryption levels and privacy protections.
Encryption Levels
Encryption is like a secret code that hides your data from prying eyes. Imagine sending a letter in a locked box. Only the person with the key can open it. That’s what encryption does for your online information.
| Proxy | VPN |
|---|---|
| Usually no encryption | High-level encryption (AES-256) |
| Basic protection for browsing | Strong protection for all internet traffic |
Most proxies don’t offer encryption. They simply act as intermediaries, forwarding your requests to the internet. This means your data is still visible to potential hackers. On the other hand, VPNs wrap your data in a high-level encryption layer. For instance, AES-256 encryption is so secure that even supercomputers would take years to crack it.
Privacy Protections
Privacy is a big concern in today’s world. We all want to keep our online activities to ourselves, right? Let’s see how proxies and VPNs handle your privacy.
- Proxy: Masks your IP address to some extent, hiding your location.
- VPN: Completely hides your IP address and provides anonymity by creating a secure tunnel.
Proxies can hide your IP address, making it seem like you’re browsing from a different location. However, they don’t offer much beyond this. VPNs, however, go the extra mile. They not only mask your IP address but also create a secure tunnel for all your internet traffic. This tunnel is encrypted, ensuring that nobody can see what you’re doing online. Even your Internet Service Provider (ISP) is kept in the dark!
So, which one should you choose? If you’re just looking to bypass geographical restrictions, a proxy might suffice. But if you’re serious about your online security and privacy, a VPN is the way to go. After all, who doesn’t want peace of mind while surfing the web?

Credit: nordlayer.com
Performance Considerations
When it comes to choosing between a proxy and a VPN, understanding performance considerations is crucial. Both proxies and VPNs serve to protect your online privacy and security, but they do so in different ways. In this section, we will explore how each of these tools affects your internet speed, latency, and bandwidth usage. Let’s dive in and see which one might be the better fit for your needs.
Speed And Latency
Speed and latency are critical factors when considering a proxy or a VPN. Your internet experience depends largely on these two elements.
Proxies: Generally, proxies tend to offer faster speeds compared to VPNs because they do not encrypt your data. This lack of encryption means less processing time is required, resulting in quicker connections. However, the speed can vary based on the server load and the distance between you and the proxy server.
VPNs: VPNs typically have slower speeds compared to proxies because they encrypt your data, which adds an extra layer of security but also requires more processing power. This encryption process can introduce latency, especially if you are connecting to a server that is far away. However, some high-quality VPNs use optimized servers to minimize this impact.
In a nutshell, if speed is your top priority, a proxy might be the way to go. But if you need enhanced security and privacy, the slight speed trade-off with a VPN might be worth it.
Bandwidth Usage
Bandwidth usage can also differ significantly between a proxy and a VPN.
Proxies: Since proxies do not encrypt data, they generally consume less bandwidth. This can be beneficial if you have a limited data plan or if you need to manage your bandwidth usage carefully. However, because proxies do not offer the same level of security as VPNs, your data could be more vulnerable to interception.
VPNs: VPNs, on the other hand, use more bandwidth due to the encryption process. This encryption ensures that your data is secure, but it also means that more data is being transferred. If you have an unlimited data plan, this might not be a concern, but for those with limited bandwidth, it’s something to keep in mind.
Ultimately, if conserving bandwidth is essential for you, a proxy might be more suitable. But if you prioritize security and don’t mind the additional bandwidth usage, a VPN is a better choice.
Choosing between a proxy and a VPN involves balancing speed, latency, and bandwidth usage based on your personal needs. Consider what you value most in your online experience and make an informed decision accordingly.
Accessibility And Compatibility
When diving into the world of online privacy and security, it’s essential to understand the differences between proxies and VPNs, especially in terms of accessibility and compatibility. Both tools serve distinct purposes and offer unique benefits. Let’s explore how they stack up against each other in these two crucial areas.
Device Compatibility
When it comes to device compatibility, VPNs generally have the upper hand. VPN services are designed to work on a wide range of devices, including:
- Computers (Windows, Mac, Linux)
- Smartphones (Android, iOS)
- Tablets
- Smart TVs
- Gaming Consoles
With VPNs, you can usually install dedicated apps or configure your device settings to use the VPN, ensuring comprehensive protection across all your gadgets. In contrast, proxies are typically more limited. While they can be set up on browsers and some applications, they don’t offer the same level of integration across different devices.
Geographical Restrictions
Have you ever been excited to watch a show only to find it’s not available in your country? This is where VPNs and proxies can help, but they do so in different ways.
VPNs excel at bypassing geographical restrictions. They allow you to connect to servers in various countries, effectively masking your IP address and making it appear as though you’re browsing from another location. This is especially useful for accessing:
- Streaming services like Netflix, Hulu, and BBC iPlayer
- Region-specific websites and content
- Online services unavailable in your country
Proxies, on the other hand, can also help you access restricted content, but they are often less reliable. Many websites can detect and block proxy servers, and they don’t offer the same level of encryption and security as VPNs. So, while a proxy might help you bypass a simple geo-block, it might not be as effective for more robust restrictions.
In summary, both proxies and VPNs have their own strengths and weaknesses in terms of accessibility and compatibility. VPNs offer broader device compatibility and are generally more effective at bypassing geographical restrictions, making them a more versatile choice for most users. Proxies, while useful in certain situations, might not provide the same level of convenience or security.
Still unsure which one to choose? Reflect on your specific needs and consider what devices you use most often and what types of restrictions you frequently encounter. This will guide you toward the best option for your unique online experience.
Cost Factors
Understanding the cost factors of proxies and VPNs is crucial for making an informed choice. This section will delve into the financial aspects of both technologies. We will explore free versus paid options and conduct a cost-benefit analysis.
Free Vs Paid Options
Both proxies and VPNs offer free and paid versions. Free proxies can be tempting but often come with risks. They may lack security and can be unreliable. Paid proxies provide better speed and reliability. They also offer enhanced security features.
Free VPNs share similar issues. They may have limited servers and slower speeds. Paid VPNs offer more server locations and faster connections. They also come with better privacy protections.
Cost-benefit Analysis
When analyzing costs, paid options often provide better value. Paid proxies and VPNs offer more features and greater reliability. They also ensure better security and privacy. Free options might save money but can compromise performance.
Investing in a paid proxy or VPN can be worthwhile. It enhances your online security and browsing experience. Weigh the costs against the benefits to find the best solution for your needs.
Choosing The Right Option
Understanding the difference between a proxy and a VPN is essential. A proxy hides your IP address for basic privacy. A VPN encrypts your data, providing more security and privacy online.
Choosing between a proxy and a VPN can be tough. Each has its unique benefits and drawbacks. Your choice should depend on your specific needs and circumstances. Some users prioritize security, while others need faster connection speeds. Let’s dive into how to assess your needs and some recommendations for making the right choice.Assessing Your Needs
First, understand your primary reason for using a proxy or VPN. If you need better security and privacy, a VPN is ideal. It encrypts your data and hides your IP address. This makes it harder for hackers to access your information. If you need to access geo-blocked content, both proxies and VPNs can help. A proxy server can change your IP address but does not encrypt your data. This makes it faster but less secure than a VPN. Consider your budget. VPNs usually cost more but offer better security and features. Proxies are often cheaper or free but come with fewer benefits.Recommendations
For maximum security and privacy, go with a VPN. It will protect your data and keep your online activities private. Choose a reputable VPN provider with good reviews. For faster speeds and basic web browsing, a proxy might be enough. Look for a reliable proxy service that offers good performance. If you need to bypass geo-restrictions, both options can work. A VPN is better for streaming services like Netflix. Proxies are suitable for accessing websites blocked in your region. Assess your needs carefully before making a choice. This will ensure you get the best solution for your specific requirements. “`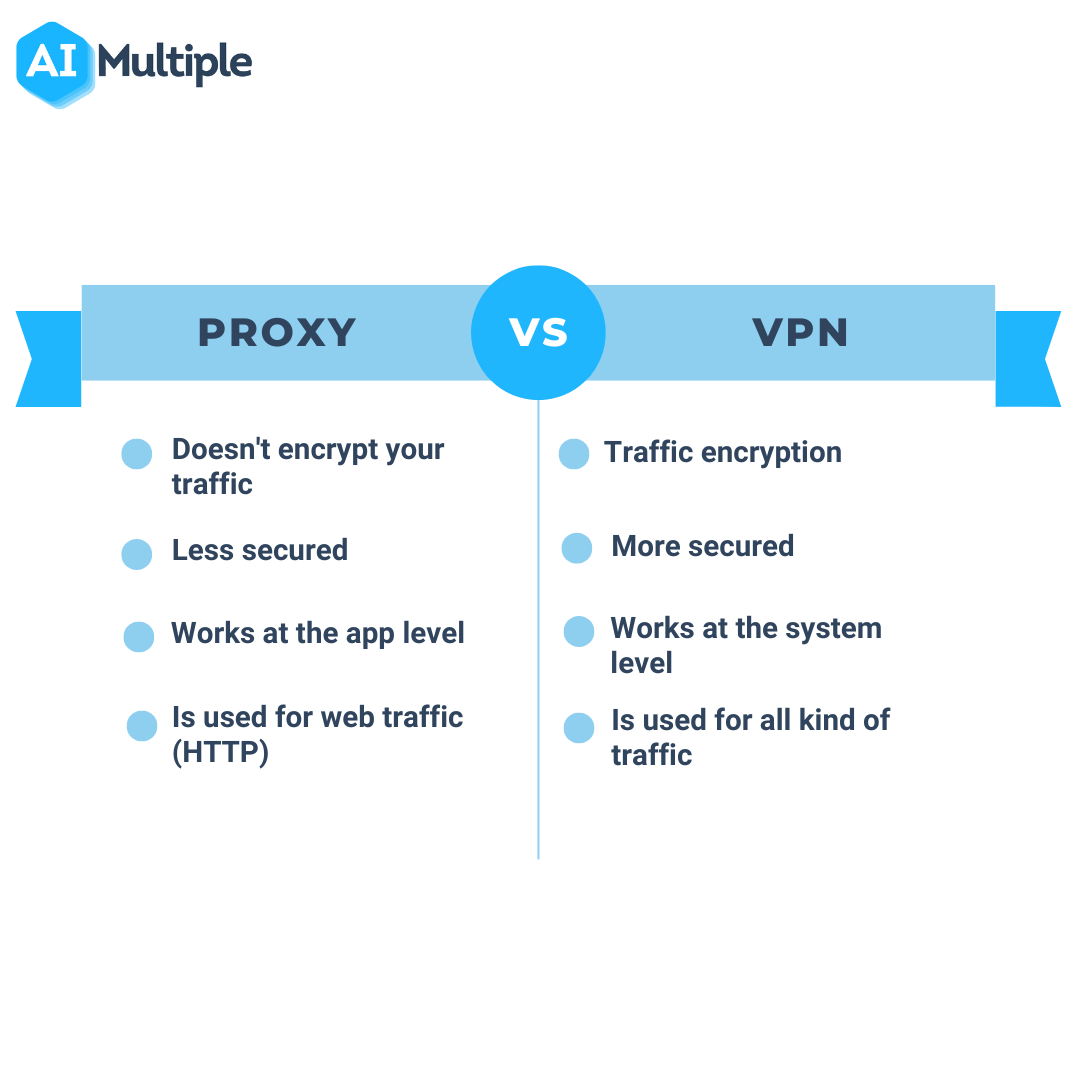
Credit: research.aimultiple.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Better, Proxy Or Vpn?
VPN is better for security and privacy. It encrypts your data, protecting your online activities from hackers. Proxies are faster but offer less security.
Why Does Netflix Say You Seem To Be Using A Vpn Or Proxy?
Netflix detects that you might be using a VPN or proxy to access content not available in your region. Disable these services to continue streaming.
Can I Use My Vpn As A Proxy?
Yes, you can use your VPN as a proxy. Most VPN services offer proxy settings. This allows you to route your internet traffic through their servers, providing an extra layer of security and anonymity. Check your VPN provider’s settings for proxy options.
Why Should You Not Always Use A Vpn?
Using a VPN can slow down internet speed and limit access to local content. VPNs may also be illegal in some regions.
Conclusion
Choosing between a proxy and a VPN depends on your needs. Proxies offer basic privacy, but VPNs provide stronger security. VPNs encrypt your data, making it safer. Proxies are often faster but less secure. For sensitive tasks, VPNs are the better choice.
For simple browsing, proxies can suffice. Both tools enhance online privacy. Evaluate your requirements before deciding. Understanding these differences helps you make an informed choice. Stay safe and secure online.
